Desalination & Climate Changes
Many have heard the popular adage of the Ancient Mariner “ Water Water Everywhere but not a Drop to Drink “. Nowadays around 300 million people are provided water from desalination plants worldwide and presently there are almost 20,000 such facilities available with varying desalination capacity and the fresh water so obtained is piped to municipal reservoirs. . The earliest commercial scale desalination plants were constructed in the sixties . Increasing population exerts pressure on aquifers and underground and sub surface water reservoirs and sources. While fresh water sources are facing depletion toxic elements from mining , urban waste and sewage and effluence from factories and dumping of lithium batteries continues to pollute water reservoirs.
Reduced snowfall over mountains is causing aridification and the same is attributable to climate change. Drought is a recurring condition in California . River reservoirs are drying up. Currently there are 11 desalination (desal) plants in California and 10 more are in the pipeline. Australia after suffering from the consequence of droughts embarked on a desalination plant spree. The city of Melbourne produced its first water in 2017 from a desal plant and the cost incurred was $ 3.5 billion to build which only provides a third of the water requirements of the city.
Cost of desalination
 Courtesy Discover Magazine
Courtesy Discover Magazine
As a result of rapidly evolving technology the cost of desalinated water is drastically reducing especially when compared to the cost of other sources and is said to have dropped by almost 50 % in the last 2 – 3 decades. In California the local authorities pay $1 ,200 for an acre-foot of water obtained from the rivers and runoffs whereas the cost of an acre foot of fresh water from the desal Carlsbad plant costs around $ 2,200 for an acre foot. The cost of an acre foot of desal water from brackish water is variable and the range is $ 1,000 to $ 2,000.The US state of Texas is constructing a desal plant which will produce 30 million gallons /day from brackish water. The lower cost of brackish based desal is on account of a significantly lower concentration of solid matter then in sea water.
Environmental Concerns & UN
 Courtesy Los Angeles Times
Courtesy Los Angeles Times
Desalination is an energy intensive process and requires vast amounts of energy which in some places is conveniently provided by fossil fuels. The greenhouse gas phenomena is pronounced in the Gulf region where a significant proportion of desal takes place and the affordability and availability of fossil fuels makes it the energy fuel of choice for desal plants .
Threat to Marine Life
Concerns abound about damage inflicted to marine life from the plant’s intake systems. Brine waste from desalination plants is toxic and according to a recent report of the UN Institute for Water, Environment and Health unless brine is diffused over large sectors of the sea it depletes the ocean of oxygen .As a pollutant brine is capable of wiping out marine life. The process of desal sucks in sea water and marine species and larger species which perish on the intake screen and fish larvae, eggs and plankton are eliminated by the process of chlorination .
Contamination concerns
The Poseidon Desal Plant in California is confronted with regulatory and environmental issues as it is located in an industrial zone already beset with a legacy of contamination concerns.Sea levels are anticipated to be raised as the coastal protection policy factors in risks of flooding of coastal areas. The politics of environmental justice further makes the policy setting complex as the environmentalist lobby decries burdening the lower strata of the community with additional water desalination charges.
Desalination Plant at Hadera, Israel
Courtesy : https://geographical.co.uk/science-environment/the-future-of-desalination
Process of Desalination
The two processes of desal are ;
- Thermal which heats up water and captures the condensation
- Reverse osmosis pushes sea water through a membrane to trap salt molecules
Distribution of Desal Plants
- A desalination plant is being constructed at a cost of $ 797 million project in the Emirate of Umm Al Quwain
- The Pacific coast biggest plant is the Carlsbad Desalination Plant in California which converts salt water into fresh water . In this plant 100 million gallons of seawater flow through semi-permeable membranes to produce 50 million gallons of water which is piped to municipal users
- Israel has five large plants in operation along the Mediterranean waters and the country’s chronic water scarcity has been overcome .A plant in Israel is claimed to be the biggest largest seawater desalination plant in the world capable of operating at a capacity of 624,000 m3/day
- In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia its Saline Water Conversion Corporation operates 27 desalination plants that produce more than 3 million cbm/day of potable water ensuring 70 % of the water supply to the cities. The water produced meets a substantial part of industry needs as well .
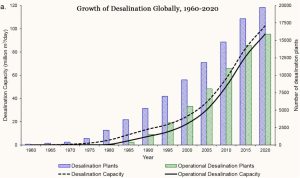
Courtesy : Yale School of Environment , https://e360.yale.edu/features/as-water-scarcity-increases-desalination-plants-are-on-the-rise
By Nadir Mumtaz


Leave A Comment